Forget the cliché – search engine optimisation (SEO) is dead definitely still exists.
And, for the record, Google can now determine the difference between a website that deserves to rank versus one that shouldn’t, better than ever before!
Long gone are the days of ranking manipulation tactics that aimed to increase keyword positions in search results. Instead, today, Google utilizes its portfolio of “algorithms” and “machine learning programs” to find, digest and display relevant pages of web results that match the need of a user’s search query.
Whether you help a bunch of clients or run your own sites, a deep understanding of how Google works can catapult website traffic and see competitors left behind – the trick is understanding how and why Google chooses to rank websites.
Before jumping into this post, it is important to first comprehensively understand what a search “algorithm” is and how Google works – let us begin.
In simple terms…
A search algorithm is a process or set of rules used by search engines to determine the significance of a web page. Algorithms are used to filter, digest and evaluate web pages to ensure search results match a user’s search query.
As the internet has exponentially grown in size, Google has had to become a data filtering machine. To deliver results that match a user’s search query, Google uses a series of complex rules and procedures (i.e algorithms) to find, filter and digest web pages from across the internet for its own “index”. It is this “index” of web pages that Google uses when displaying relevant search results.
Remember, Google is not the internet and instead should be seen as a “gateway”, helping users to find up-to-date and accurate information time and time again. As the “go-to” search engine, Google dominates the industry, processing in excess of 3.5 billion worldwide searches every day! With so much user demand and potential power to make or break websites and businesses, it is clear that investing the time to co-operate and impress Google’s algorithms is a win-win situation for you or your client’s websites.
Let’s move on to learning more about four of Google’s most-important ranking algorithms and what you can do to get in their good books.
Panda algorithm 
TLDR: Panda loves to read and digest information. Try to create content that answers user search queries and never copy from others. Grab Panda’s attention with long-form content that’s ten times better than the competition but don’t bulk pages out with “fluff” if there’s no need. If you run an eCommerce site, focus your effort around building high-quality product pages that deserve to rank.
What is Panda?
First released in February 2011, Google’s Panda algorithm creates a webpage “score” based on a range of quality criteria which is mainly focused around content and is still regularly updated. Originally built to behave like a “ranking filter” to sieve sites with plagiarized or thin content from search results, Panda was later incorporated into the core ranking algorithm in early 2016. The algorithm’s content focused metrics have continued to provide an important backbone within Google’s ranking factors that help to provide search results that deliver useful information time after time, keeping Google as the “go-to” search engine on the web.
How does it work?
Just like the animal’s coat and markings, Panda likes to see thick, quality content that is unique. The algorithm understands content duplication on a page by page level (both internally & across other sites) and certainly doesn’t appreciate keyword stuffing. Websites with lots of duplicated pages or poor quality content may receive ranking decreases which in turn will reduce traffic as Google starts to devalue the domain. Pages with high-quality content that answer user search queries should be rewarded with higher ranking positions. However, this is not always the case, especially in online markets where there is lots of competition and other ranking factors are given more precedence such as domain equity and backlinks.
How to make sure you don’t get penalized
Webmasters, SEO managers and website owners can all make a difference when it comes to staying on the right side of Panda. As the algorithm is continually updated, it’s important to always carry out best practice content strategies to protect your website from any future updates. Follow these three content strategies to stay ahead of the game…
- Make sure the content you publish is 100% unique – never “spin” or copy content.
- Don’t create pages with thin or duplicated content – always try to write a minimum of 200 words per page. Writing “some” content is always better than no content.
- In the case where pages with no content can’t be updated with more text, you should consider delisting them from Google’s index to reduce negative exposure. This can be carried out through editing a website’s robots.txt file or editing settings within SEO plugins such as Yoast SEO.
Here’s a great web page example where Panda might be triggered due to there being little to no page content. The page is code-heavy and provides no value being in Google’s index.
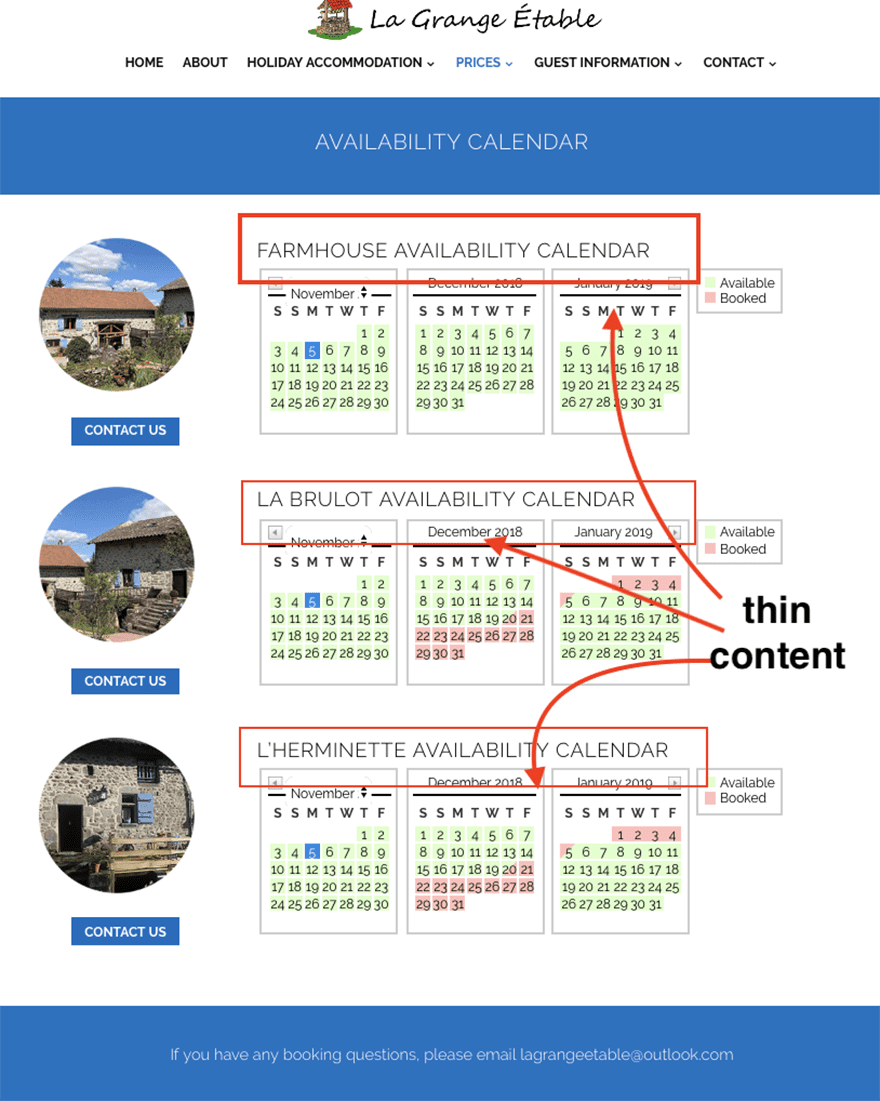
Pro tip: For pages where little to no content exists – try incorporating content based around answering common user questions or instead, de-index these pages in your robots.txt file.
Penguin algorithm 
TLDR: Penguin loves to see trustworthy relationships between sites. Stay out of the way of Penguin’s slap through creating genuine, quality links with others across the internet. Just like in the real world, there is no quick shortcut to building strong relationships. If you are executing link building strategies, be sure to check your website’s backlinks regularly to keep your footprint clean, tidy and natural.
What is Penguin?
First released in April 2012 and later incorporated (like Panda) into the core ranking algorithm in 2016, Google’s Penguin algorithm is a real-time, location and language independent data processing filter that aims to uncover and devalue websites with backlinks that may be deemed manipulative or unnatural. Continual Penguin updates have considerably changed the SEO industry and today, engaging in outdated tactics can leave websites penalized and even delisted from Google’s index. The algorithms sole focus on backlinks now ensures SEO managers and webmasters build and attract high-quality backlinks that are seen as a strong “vote of confidence” between websites.
How does it work?
Just like penguin huddles, the algorithm likes to see trusted “link” relationships around websites. Despite industry noise, high-quality link building is still one of the most important tactics to drive ranking increases and Penguin keeps a close eye ensuring websites do not manipulate the system. Running in real-time, Penguin kicks into action when sites build threatening volumes of links in a short space of time, pay for sponsored links or carry out spammy black-hat techniques. The algorithm also monitors “anchor text” profiles as these can also be cleverly orchestrated to influence rankings. Manipulating Penguin through executing unethical tactics could result in a huge loss of website traffic.
How to make sure you don’t get penalized
In the words of Google – “Avoid tricks intended to improve search engine rankings. A good rule of thumb is whether you’d feel comfortable explaining what you’ve done to a Google employee”. To stay in Penguin’s good books, you should build links that you want to exist and not just because you have a short-term end goal. If you are a link building “newbie” or want to change your ways, remember to always approach link building with the motto of “link earning”. This means building links you would never want to remove.
Noticed a recent drop in traffic or worried about being penalized? Stay calm, you can take action before it’s too late. Paid backlink profiling tools such as Majestic, ahrefs and Link Research Tools will help you evaluate a website’s footprint and highlight areas to improve.
To quickly gauge spammy link levels surrounding a domain, you need to review its anchor text breakdown. Using Majestic’s tool, here’s a great example of a site that looks to have an unnatural top 10 list highlighting lots of spammy links.
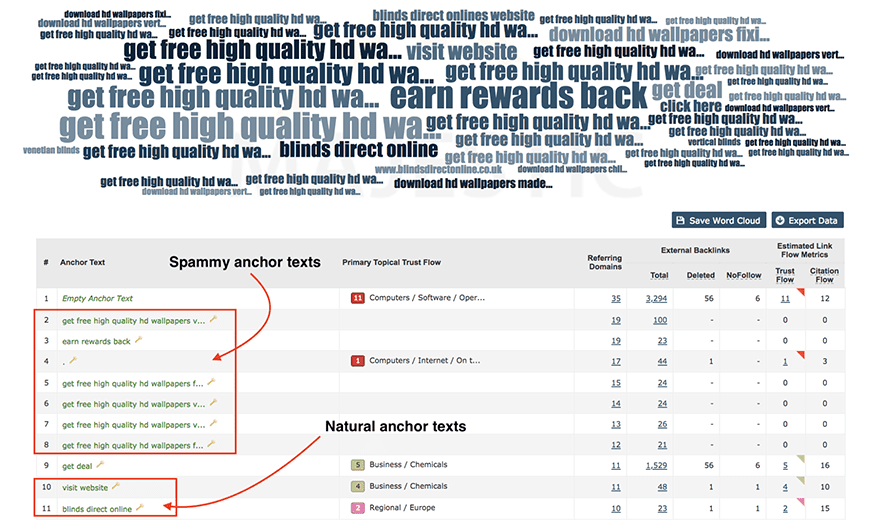
Pro tip: Anchor text profiles should be natural and contain mainly branded, product or service related keywords. If you spot spammy or unrelated anchor text in your top 10 list, this could be a cause for concern and should be investigated immediately.
Hummingbird algorithm 
TLDR: Hummingbird is ready and waiting to feed on your website like sweet nectar. Try attracting attention by creating pages that match the “search intent” of the user. Explore possible synonyms and target longer tail keywords with less competition. Learn from competitors that may be outranking you. If you struggle to write content, answer common customer questions in a natural and engaging way – here’s a great example.
What is Hummingbird?
First released in September 2013, Google’s Hummingbird algorithm significantly changed the way the search engine interpreted user queries and rewards websites who answer a user’s search phrase. The introduction of Hummingbird shifted websites to focus on matching a user’s “search intent” rather than simply trying to rank for a keyword or phrase. The ultimate goal for this brand new algorithm was to help Google better understand the “what” behind a user search query, rather than displaying results based on a broad level, keyword basis. In short, Hummingbird helps users find what they want alongside enabling Google to find, filter and display results that are more precisely focused on the meaning behind a query.
How does it work?
Just like the bird it’s named after, the algorithm is instantly recognisable every time a Google results page is displayed. You can see Hummingbird in action at the bottom of Google where other “theme-related” results are shown that do not necessarily contain the keywords from the original search query. Hummingbird is not a penalty-based algorithm. Instead it breaks down long, conversational queries to unpick the “intent”, takes into consideration wider website relevancy of each search, and rewards sites that use natural synonyms and long-tail keywords. Hummingbird not only understands how different web audiences behave, the algorithm can also quickly recognise what a searcher is looking for, through displaying related suggestions in the search box prior to displaying results.
For unrecognized search queries (did you know – around 15% of all daily Google searches have never been searched before!?) Google harnesses the power of it’s artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm – Rankbrain. Released in April 2015, this machine learning supercomputer not only deciphers the “intent” behind new queries, it also filters the displayed results accordingly. You can read more about Google’s Rankbrain algorithm here.
What can I do to catch its attention?
Ultimately, website’s that implement a cross-combination of the algorithms criteria should see significant ranking increases overtime. If your site is currently ranking poorly within your niche, there is a high chance that Hummingbird has some influence over your positioning. Try to build strong “Hummingbird friendly” foundations at the start of any digital project as this will pay dividends. This can include; incorporating conversational answers to questions within content (here’s a great example of this), including synonyms and targeting long-tail keywords or phrases. To find synonyms, Ubersuggest is a great place to start. Furthermore, Google’s related search results are always worth looking at and don’t forget to check out the competition that’s ranking above you.
Here’s a great example of an eCommerce website that generates content based around common customer questions. This helps Hummingbird to understand website relevancy.
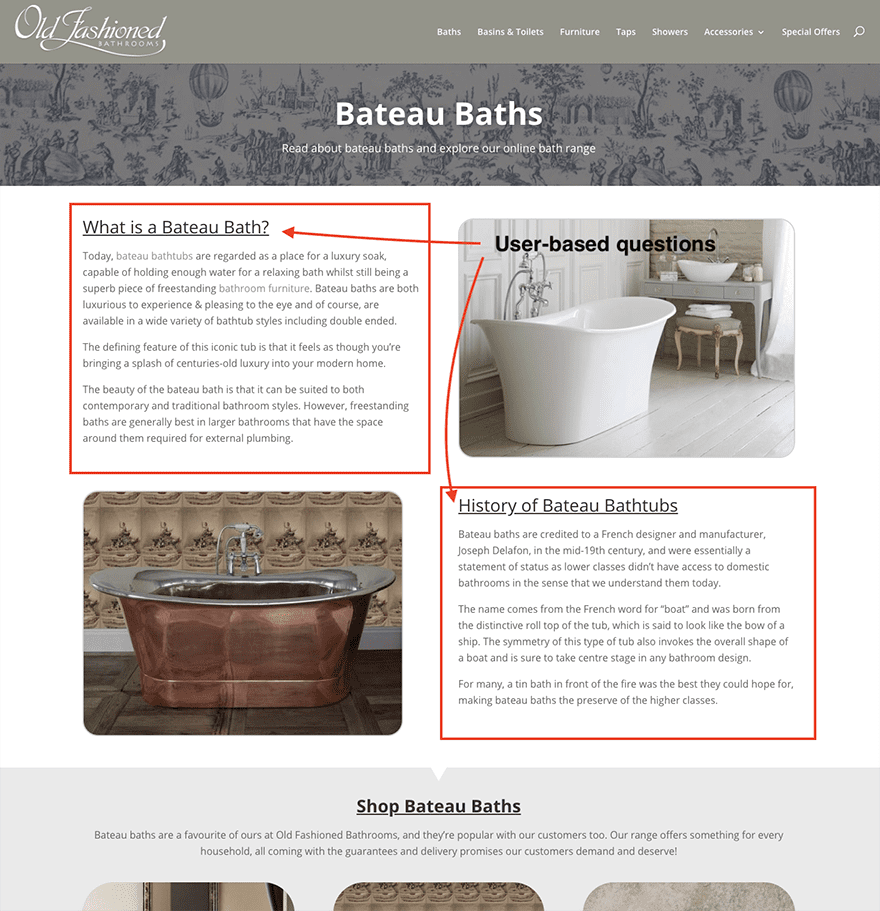
Pro tip: Before writing or creating new web pages, answer the following questions: what is the purpose of this page? What is it trying to target? Scoping the purpose early gives time to research possible synonyms, long tail keywords and to explore the competition.
Pigeon algorithm 
TLDR: Pigeon is ready to deliver better local results when you start feeding it. Take advantage of Google My Business and get listed in some genuine and trusted online local directories such as Yelp. When creating content, try to use text and imagery that is distinctively associated with a location or area. If you run a service based business, make sure you are generating user reviews – this will help you stand out from the local crowd.
What is Pigeon?
First released in August 2013, Google’s Pigeon algorithm was launched to provide better results for local searches. Prior to Pigeon, Google’s local search results produced a mixed bag of information and an update was needed to incorporate both location and distance as important factors when displaying results. Subsequently, Google reduced the number of displayed local business results from 7 to 3, making local exposure even tougher. However, the algorithm effectively combined Google search results with Google Map searches and set in motion a more cohesive way for websites to rank organically for local searches.
How does it work?
Just like the navigational ability of homing pigeons, the algorithm relies heavily upon gathering data on a user’s location and distance before displaying search results (this data must be shared with Google otherwise results are based on keywords only). Pigeon is a great example of Google in a “mobile-first” world, striving to deliver relevant search results during every possible interaction. Although it is not possible to manipulate where potential customers may use Google, Pigeon now takes more notice of local directory listings, reviews and local reputation when ranking results. This algorithm does not penalize websites, instead it focuses on giving prominence to those sites that deserve to be listed locally.
Note: Pigeon is only currently affecting search results in the English language.
How to make sure you get noticed locally
Pigeon loves to see local relationships and rewards data consistency across the internet. It is important to focus on foundational SEO that incorporates location based keywords and be sure to take advantage of Google My Business listings. If you want to really impress Pigeon, work on building high-quality directory listings with consistent data, and work hard to establish positive user-generated reviews. With so many local businesses now heavily relying on Google to drive foot traffic and sales, a deep understanding of this algorithm will help carve some much-needed space between the local competition.
Here’s a great example of a local business that has taken advantage of Google My Business and publishes content based around local keywords. This helps Pigeon to understand the location of potential customers.
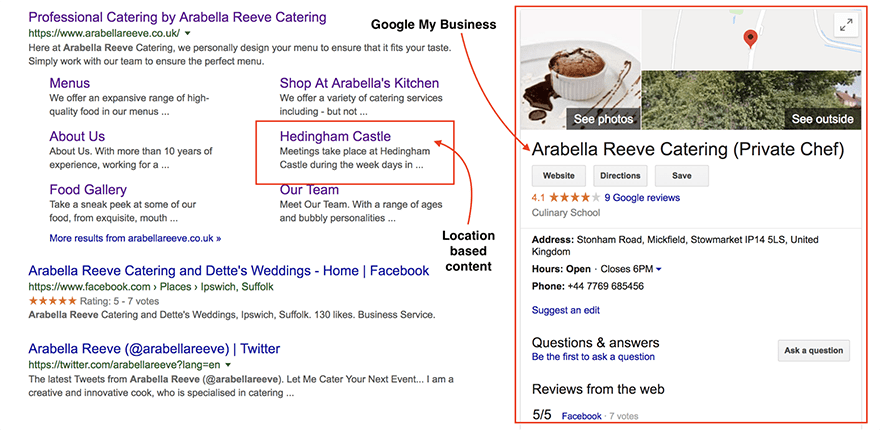
Pro tip: For websites who heavily rely on local traffic, it’s important to treat local SEO much like your local reputation. Remember to provide the same data across the internet, be serious about reviews, and help the Pigeon algorithm to understand your audience location with targeted content.
Conclusion
Gaining a deeper understanding of how Google ranks websites helps you spend time in the areas where change can most impact performance. It’s important to remember that increasing website rankings is a long process that requires strategic guidance, and meeting the criteria of Google’s algorithms can sometimes be a tricky process. However, at the same time, aligning with the expectations of each algorithm self-generates the strategy needed to succeed online. Executing tactics that aim to impress Google’s algorithms is always the best strategy as they ultimately create the rules that can make or break any future achievements.
It’s inevitable that Google will be forever updating and tweaking their algorithms. Even as the most dominant internet search engine, Google continually rocks the boat to disrupt the SEO industry, improve search results and to stay ahead of its own competition. This is because the moment a user does not get the answer they are looking for, they may quite possibly use another search engine. Over time, if searches on Google decline, so does their huge revenue from Google Ads, so it’s in the search engine’s best interest to maintain and improve search results on an ongoing basis.
The four algorithms covered in this post are only part of Google’s ranking algorithms. In total, there are over 200 ranking factors that are examined across a wide range of sophisticated algorithms and machine learning programs. It is ultimately these algorithms that decide where a web page should rank in search results. Continual updates from both technical and behavioral perspectives requires the essential need, to stay updated overtime.
If you’re interested in keeping up to date with Google’s latest algorithm updates and making sure your client’s or your own sites climb the search rankings and avoid potential traffic losses, here are a few resources to bookmark:
- MOZ Google Updates – displays updates stretching back to the year 2000
- SEMRUSH Sensor – shows a daily graph of search ranking velocity
- Search Engine Land – highlights Google news, updates and press releases
The post A Beginner’s Guide to Google’s 4 Most-Important Ranking Algorithms appeared first on Elegant Themes Blog.
