There are a lot of ways you can secure your data online. If you want to be pro-active, two of the best solutions you can use are a proxy server or a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
However, to choose between a proxy vs a VPN, you need to understand how both options work. In this article, we’ll talk about what sets them apart, the downsides of using either a VPN or a proxy, and how to choose between them. Then we’ll introduce you to a few options for setting up each.
Let’s get to it!
Proxy vs VPN: What’s the Difference?
A proxy server relays your browser’s or application’s requests onto their destination. While it does so, it cleans those requests of any identifying digital footprints, such as your IP address, where you’re located, and more.
However, proxy servers work at the application level. This means you can use a proxy server to route a specific browser’s activity, but not that of your whole Operating System (OS).
A VPN, on the other hand, routes all of your online traffic through a server. That includes activities such as File Transfer Protocol (FTP) connections, OS updates, third-party app downloads – everything. This offers the same advantage of “cloaking” your identity and the source of the traffic, but with a higher degree of privacy than a proxy.
In practice, you can configure proxy servers to route most of your system’s traffic. Unfortunately, some applications are not easy to work with when using proxy servers.
Generally speaking, VPNs do a better job of protecting your personal information. However, that’s not the only reason why you’d want to use either a proxy server or a VPN.
When to Use a Proxy vs VPN
Proxy servers are ideal for situations where you need to monitor internet activity and ensure that users can’t access specific apps or websites. Two great examples of such circumstances would include:
- Learning institutions. Often, schools have a massive number of devices on the same network. Without “rules”, users may abuse their connection.
- Office environments. With a proxy server, you can limit access to dangerous websites, configure a firewall, and even create caching rules to speed up browsing.
The primary advantage of proxy servers, beyond increased privacy, lies in scaling. An entire office can use a proxy server, whereas VPNs tend to have strict limits on the number of devices you can connect.
With a proxy server, you can configure the entire web experience for large-scale networks. You can set up rules to protect users and reduce the risk of malware infections.
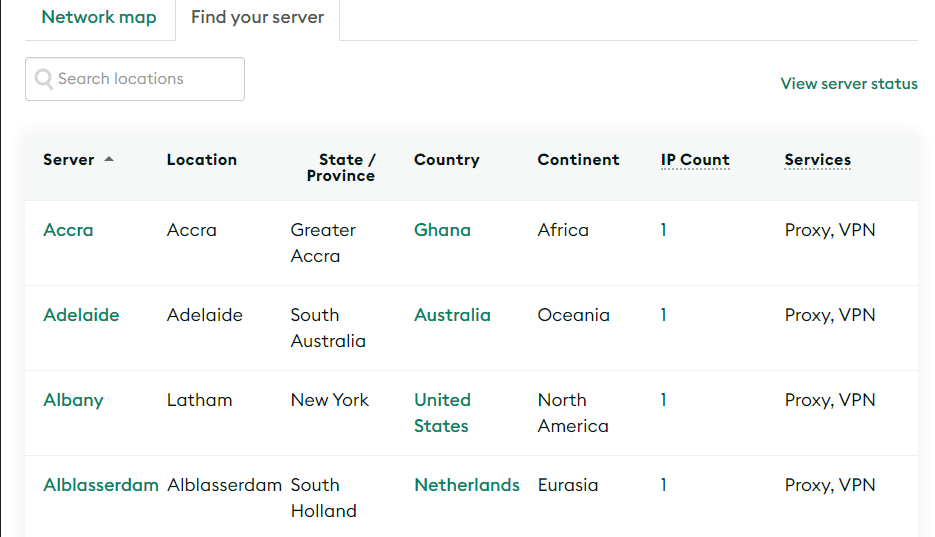
For non-work environments, you can use a proxy server to access geo-restricted content. One advantage that proxies have over VPNs in that aspect is that a lot of open proxy providers give you access to a broad number of servers:
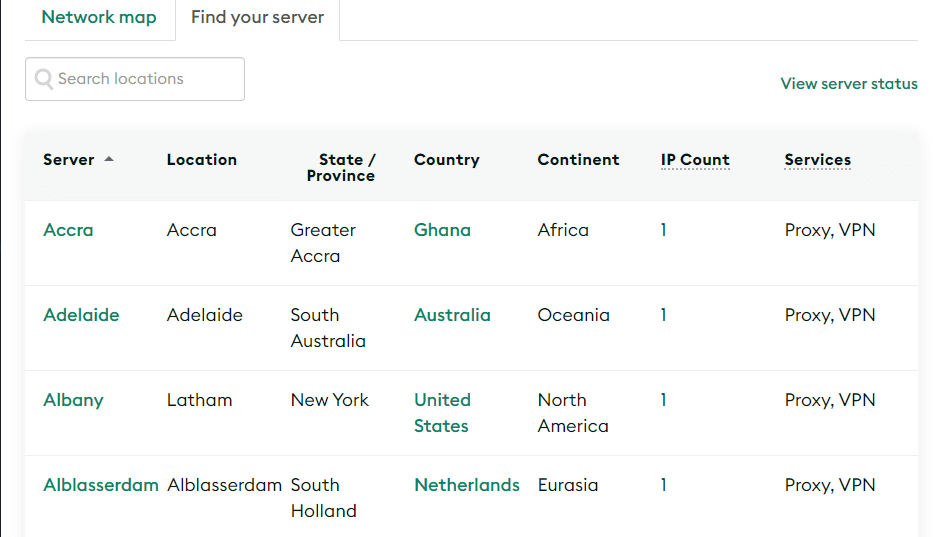
Since you can pick and choose which server to use, a proxy may give you access to a lot of content you otherwise wouldn’t be able to reach (Netflix is savvy to a lot of these tricks, however).
Keep in mind that open proxy providers work differently from what you see in learning environments or offices. In those settings, you’re probably dealing with a forward proxy server.
When to Use a VPN vs a Proxy
VPNs are all about privacy. They route and encrypt all your online activity on a specific device. This comes in handy in a variety of situations, including:
- If you use public networks regularly. Public networks are, by and large, unsafe. With a VPN, you don’t have to worry about data interception.
- For working remotely. If you’re usually working on the go and you need to connect to your company’s network, they’ll usually ask you to use a VPN. That way, they can be sure that all the data you’re working with is safe.
- For spoofing your location. If you’re connected to a VPN, all your traffic is routed through a remote server. Depending on where that server is located, you might be able to bypass regional restrictions.
Out of the office, a lot of people use VPNs to bypass torrenting and streaming restrictions. The “downside” of using a VPN for location spoofing is that most providers limit you to a specific location. If your primary goal with using a VPN is to access geo-restricted content, make sure the provider you choose enables you to switch locations.
Likewise, a lot of VPNs used shared IP addresses. That adds an extra layer of anonymity since it makes it harder to link specific users to a specific address.
When comparing proxies vs VPNs, the latter can be a bit slower. That’s because they need to route all of your system’s traffic as well as encrypt it. Proxy servers, on the other hand, can actually improve loading times.
How to Choose a Proxy Server or VPN Provider
Choosing VPN and proxy providers is a very sensitive topic. With VPNs, in particular, you want a provider that upholds the highest security and privacy standards.
As you might imagine, those providers are all too rare. With that in mind, what we can do is point you towards the resources you need to make an informed decision for a variety of scenarios:
- Choosing the most secure VPN service. By far the most comprehensive resource for VPN provider comparison is That One Privacy Site. This website compares VPNs when it comes to jurisdiction, logging, server configuration, security, and more.
- Choosing a budget VPN provider. With something as sensitive as a VPN, it’s not the smartest idea to opt for the cheapest option without any research. In this roundup, you can find a list of the VPNs we do recommend, including pricing information.
Proxy servers are a trickier subject. A lot of free proxy servers on the web work perfectly if you just want occasional access to restricted websites. In a lot of cases, all you have to do is enter a URL, choose a location, and let the service do the work for you.
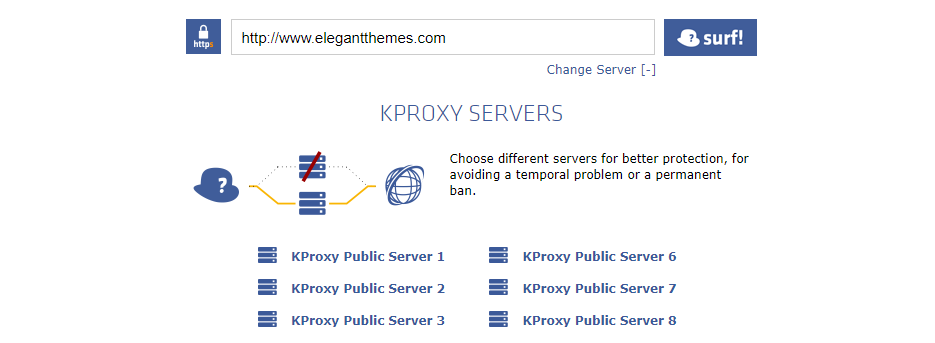
This type of proxy won’t cut it in an office environment, however. To reap all the benefits of proxy servers that we’ve discussed, you’ll want to set up your own. For that, an open-source solution such as Squid is the best option:

Setting up and configuring a proxy server for an office falls squarely within the domain of a sysadmin’s duties. For less strict environments, you can try configuring one on your own. However, for a business, you might want to hire a professional.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between and proxy vs a VPN is key for protecting your data. If you tend to work remotely or with sensitive information, then a VPN is the right option for you. Sometimes, they might not be the fastest option, but they’re by far the more secure choice.
Proxy servers, on the other hand, are perfect for office environments where you need to monitor web activity. They’re also the best choice for bypassing geo-restricted content, as providers often enable you to switch between multiple servers.
Do you have any questions about how to choose between a proxy vs a VPN? Let’s talk about them in the comments section below!
Article thumbnail image by Elaine333 / shutterstock.com
The post Proxy vs VPN: Which is Right For You? appeared first on Elegant Themes Blog.